DFT studies of Ni cluster on graphene surface: effect of CO2 activation†
Abstract
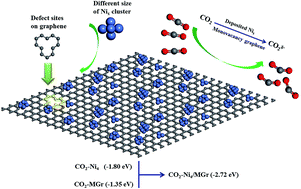
CO2 capture, storage, sequestration (CCS), and utilization (CCU) are regarded as the most effective way to slow the pace of global warming. In our present work, the structural stability and catalytic properties for adsorbing CO2 on the surface of isolated Ni clusters and 5–8–5 monovacancy graphene (MGr) supported Ni clusters have been investigated using density functional theory. The results show that, with the increasing of atomic number, the structure of isolated Ni clusters tended to be stable and the structural parameters approached to that of metal crystal. In addition, when Ni clusters deposited on the MGr surface, the Ni–Ni bond generally elongated, indicating activation of the isolated metal clusters by graphene. Adsorption energies of CO2 onto Ni4 cluster and MGr were −1.80 and −1.35 eV, respectively, while the value reached −2.72 eV when CO2 adsorbed on Ni4 cluster modified with MGr (Nix/MGr). The phenomenon indicates that the adsorption capacity of CO2 were significantly improved by depositing Ni clusters onto MGr surface and the system tended to be more stable. According to the analyses of Mulliken charge, electrostatic potential (EP) and partial density of states (PDOS), more electrons transferred from Nix cluster to the region of CO2 and MGr when CO2 adsorbed on Nix/MGr. The mechanism was proposed for CO2 adsorption on Nix/MGr at the molecular level. It is of great significance to devise high activity catalyst of CO2 storage and hydrocarbon production from CO2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...