Effects of protein species and surface physicochemical features on the deposition of nanoparticles onto protein-coated planar surfaces†
Abstract
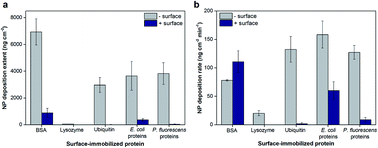
Proteins are often an important component of many bulk surfaces in biological and environmental systems that are coated with complex organic compounds that may also interact with NPs. We investigated the deposition of bare hematite NPs onto various proteins adsorbed on either negatively- or positively-charged bottom surfaces. Bovine serum albumin (BSA), lysozyme, and ubiquitin were used as model proteins and total protein extracts from two bacterial strains, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens, were used as complex protein mixtures. The NP deposition extents and rates were shown to be significantly different depending on the protein. The maximum difference observed was 8.6 ± 3.2 fold between E. coli and P. fluorescens proteins adsorbed onto positively-charged planar surfaces. These differences in NP deposition characteristics are attributed to the differences in physicochemical features of the topmost surface of the protein layer, such as the amino acid profiles, surface charge, and hydrophilicity. Such differences were likely driven by differences in species, orientation, and conformation of the adsorbed proteins. In particular, NP deposition was driven by various combinations of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. This study indicates that NP deposition onto surface-adsorbed proteins is an important mechanism in protein–NP interactions and that the deposition is strongly dependent on both the conformation and chemical characteristics of the adsorbed protein layer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...