Density functional theory and liquid chromatography-multistage mass spectrometry to characterize raltitrexed photo-degradation mechanisms†
Abstract
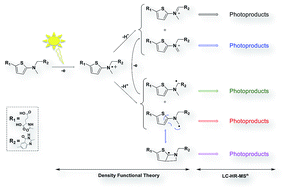
Used in cancer chemotherapy, raltitrexed (RALTI) is an antimetabolite drug acting as thymidylate synthase inhibitor. A photostability study of the antineoplastic drug in aqueous solution and under aerobic conditions is presented. The investigation involved its decomposition under homogenous photolysis making use of the simulated sunlight as exposition source and the identification of the photoproducts formed by high performance liquid chromatography-high-resolution multistage mass spectrometry (LC-HR-MSn). Structural information, combined to density functional theory calculations, has enabled elucidating the main photodegradation pathways of aqueous RALTI. One-electron oxidation was shown mainly responsible for the initiation of RALTI photodegradation in pure water involving specifically the amino thiophenate moiety. In the absence of photocatalysts, electron-transfer seems to mainly proceed through RALTI autoionization, responsible for the formation of RALTI α-amino radicals and RALTI iminium ions, intermediates able to perfectly substantiate the origin formation of most of the photoproducts generated under solar irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...