Characterization of a designed synthetic autotrophic–heterotrophic consortia for fixing CO2 without light†
Abstract
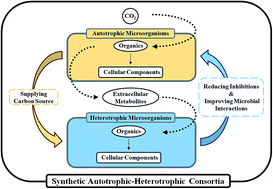
Microbial interactions are important for metabolism, and they improve metabolic substrate types and metabolic efficiency. To discover microbial combinations with high CO2 fixation efficiencies, a series of synergistic microbial consortia of increasing diversity and complexity were devised using chemoautotrophic strains, including Ochrobactrum, Stenotrophomonas, Castellaniella, and Sinomicrobium strains, which were isolated from a non-photosynthetic microbial community (NPMC) with CO2 fixation capacity. Addition of a small inocula of NPMC universally improved the CO2 fixation efficiencies of the consortia by up to 10-fold, while the CO2 fixation efficiencies of most multimember consortia were similar to those of single strains. An analysis of the microbial community structure revealed that both autotrophic–autotrophic microbial interactions and autotrophic–heterotrophic microbial interactions occurred in the synthetic microbial consortia. Ochrobactrum and Castellaniella strains were crucial for autotrophic metabolism, while Lysinibacillus and Pseudomonas strains were crucial for heterotrophic metabolism. These devised microbial consortia have potential applications in addressing environmental issues.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...