Silymarin nanoparticles through emulsion solvent evaporation method for oral delivery with high antioxidant activities, bioavailability, and absorption in the liver†
Abstract
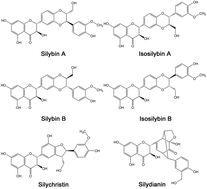
Silymarin (SM), a well-known hepatoprotective drug, is widely used to treat liver disorders. However, its application was seriously restricted because of its poor aqueous solubility. In this study, silymarin nanoparticles (SMNs) were prepared through emulsion solvent evaporation and freeze-drying methods to improve their solubility. SM nanoemulsion was optimized through a single-factor experiment. SMNs with MPS of 107.1 ± 13.7 nm were produced under optimum conditions. These SMNs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermal gravimetric analysis to determine their solvent residue, equilibrium solubility, dissolution rate, stability, antioxidant activity, bioavailability, and absorption in the liver. The results showed a smaller particle size and lower crystallinity in SMNs than those in raw SM. The solubility of SMNs was 4.87 times higher in simulated gastric fluid and 3.70 times higher in simulated intestinal fluid than that of raw silymarin. In addition, the residual amounts of chloroform and ethanol were separately less than the amount indicated by the international conference on harmonization limit for class II. The antioxidant activity after incubation with plasma in vitro of SMNs was higher than that of raw SM. Moreover, the oral bioavailability of SMNs was 3.66 times higher than that of raw SM. The silybin absorption of SMNs was also significantly higher than that of raw SM in the other organs, and very high silybin concentrations were observed in the liver with a long retention time. Overall, the results concluded that SMNs can be applied in oral delivery formulations and show potential application value for liver disease therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...