Neuroprotective effects of nitidine in Parkinson's disease models through inhibiting microglia activation: role of the Jak2–Stat3 pathway
Abstract
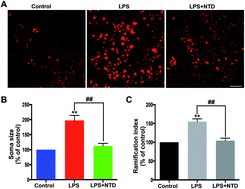
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder; currently, no effective therapy is available to halt the progression of this disease. Neuroinflammation significantly contributes to the pathogenesis of PD. Recent studies have demonstrated that nitidine possesses anti-inflammatory activity. However, the role of nitidine in neuroinflammation of PD and the mechanism of its action, if any, are still unknown. In the present study, our results showed that nitidine significantly suppressed neurotoxin induced microglial activation in vitro. Further, we demonstrated that the inhibitory effect of nitidine on microglial activation is mediated by the Jak2–Stat3 pathway and that nitidine can suppress the nuclear translocation of p-Stat3 via enhancing the binding activity of αB-crystalline (CRYAB). Importantly, nitidine could inhibit reactive microgliosis and protect dopaminergic neurons in two Parkinson's disease animal models. Finally, our data showed that nitidine significantly improved neurobehavioral activity in PD animal models. Our results indicated that nitidine could significantly suppress microglial activation via the Jak2–Stat3 pathway and obviously improve behavioral function in PD animal models, which sheds some light on a promising therapeutic strategy for PD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...