Nonvolatile electrical switching behavior and mechanism of functional polyimides bearing a pyrrole unit: influence of different side groups†
Abstract
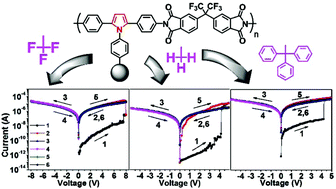
To better understand the structure–property relationships and the mechanisms of the electronic switching behavior of functional polyimides, a new series of diamines containing a pyrrole core with different side groups were designed and synthesized. Three novel, thermally stable and aromatic polyimides (Py6FPIs) containing the as-designed diamines were prepared. They were fabricated into memory devices sandwiched between an Al top electrode and an indium-tin oxide (ITO) bottom electrode by spin-coating. The polyimides exhibited high thermal stability with glass transition temperatures (Tg) around 300 °C as determined by DMA. The memory devices were found to show nonvolatile bistable write-once-read-many (WORM) memory characteristics with diverse switching threshold voltages and ON/OFF ratios, depending on the electron affinity of the pendent groups. The low-conductivity state and the high-conductivity state could be sustained under a constant bias or a refreshing voltage pulse of 1.0 V. The switching mechanism and the memory effects were finely demonstrated with the aid of molecular simulations and electronic absorption spectra of these Py6FPIs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...