Removal efficiency of MIEX® pretreatment on typical proteins and amino acids derived from Microcystis aeruginosa
Abstract
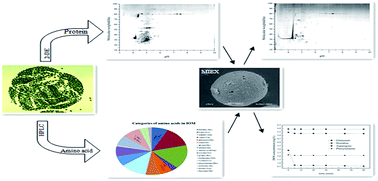
Dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) is now considered as one of the most important precursors of nitrogenous disinfection byproducts (N-DBPs), and algal cells are the main source of DON in eutrophic water sources. In this study, typical forms of DON in Microcystis aeruginosa cells were analyzed and the removal efficiency of magnetic ion exchange resin (MIEX®) treatment on typical forms of DON and the factors influencing it were also investigated. About 185 proteins and 13 amino acids were found in the intracellular organic matter (IOM) of M. aeruginosa cells. The isoelectric points (PIs) of these proteins were mostly acidic, and phycocyanin was the principal protein with a concentration of about 0.673 mg L−1. In addition, high levels of aspartic acid, histidine, tryptophan, and asparagine were also noted, which presented higher potential to produce N-DBPs during the chlorination process. The removal efficiencies of MIEX® on various amino acids and phycocyanin were quite different primarily because of their different PIs and molecular properties. The pH was noted to be the main factor affecting the removal efficiency, and common inorganic anions also had obvious influence on the removal of amino acids and phycocyanin the following order: SO42− > Cl− > HCO3−. The proteins in the IOM were effectively removed by MIEX® and only 50 proteins were found in the spectrum of two-dimensional electrophoresis. Thus, coagulation could be significantly enhanced by MIEX® pretreatment, which is one of the good alternatives to control typical DON in IOM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...