Reactivity of different surface sites with silicon chlorides during atomic layer deposition of silicon nitride†
Abstract
We studied the reactivity of different surface sites of β-Si3N4 with silicon chlorides during the first half reaction of an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process using ab initio density functional theory calculations to understand the underlying reaction mechanism. We considered three types of surface sites, NH*/SiH*, NH*/SiNH2*, and under-coordinated bare ![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) Si
Si![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–. The reactions of the silicon chlorides with NH*/SiNH2* and
N–. The reactions of the silicon chlorides with NH*/SiNH2* and ![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) Si
Si![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N– are energetically favorable, whereas the reactions are endothermic with NH*/SiH*. On
N– are energetically favorable, whereas the reactions are endothermic with NH*/SiH*. On ![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) Si
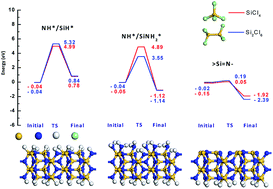
Si![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–, the silicon and chlorine atoms of the precursors easily react with the unsaturated nitrogen and silicon atoms, respectively, resulting in very low energy barriers for the reaction. However, on NH*/SiH* and NH*/SiNH2*, the reaction undergoes high energy barriers due to the dissociation of a hydrogen atom from the surface or a chlorine atom from the precursor. We further found that Si2Cl6 shows energies of reaction lower than those of SiCl4 on
N–, the silicon and chlorine atoms of the precursors easily react with the unsaturated nitrogen and silicon atoms, respectively, resulting in very low energy barriers for the reaction. However, on NH*/SiH* and NH*/SiNH2*, the reaction undergoes high energy barriers due to the dissociation of a hydrogen atom from the surface or a chlorine atom from the precursor. We further found that Si2Cl6 shows energies of reaction lower than those of SiCl4 on ![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) Si
Si![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–. By discovering the influence of surface reaction sites on ALD reactions, we designed a new 3-step ALD process to obtain the most effective surface sites for the first half reaction, and confirmed this with deposition experiments. The N2 plasma steps, prior to the introduction of a silicon precursor, reduced the saturation dose of Si2Cl6 from 107 L to <106 L and increased the growth rate from 0.59 Å per cycle to 1.1 Å per cycle, which agrees with our calculations. These results show that the reactivity of the surface sites plays a very important role to determine the thermodynamics and kinetics of ALD processes.
N–. By discovering the influence of surface reaction sites on ALD reactions, we designed a new 3-step ALD process to obtain the most effective surface sites for the first half reaction, and confirmed this with deposition experiments. The N2 plasma steps, prior to the introduction of a silicon precursor, reduced the saturation dose of Si2Cl6 from 107 L to <106 L and increased the growth rate from 0.59 Å per cycle to 1.1 Å per cycle, which agrees with our calculations. These results show that the reactivity of the surface sites plays a very important role to determine the thermodynamics and kinetics of ALD processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...