Label-free, homogeneous, and ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria based on target-triggered isothermally exponential amplification
Abstract
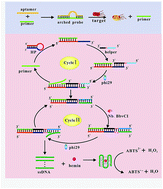
In this work, a simple, isothermal, and ultrasensitive homogeneous colorimetric sensor for pathogenic bacteria detection has been developed on the basis of target-triggered exponential amplification reaction (EXPAR). An aptamer–primer probe (arched probe) containing anti-target aptamer and a primer sequence, which is released under the challenging of target, is used for recognizing target and triggering EXPAR-based polymerase elongation. Due to EXPAR coupled DNAzyme amplification strategy, the presence of target pathogenic bacteria leads to the formation of numerous G-quadruplex oligomers in solution, which folds into G-quadruplex/hemin complexes with the help of K+ and hemin, thus generating extremely strong catalytic activity toward H2O2 and giving a remarkably strong UV-vis absorption. This work is a novel design that EXPAR coupled DNAzyme amplification technique has been integrated into colorimetric assay for detecting pathogenic bacteria. Under optimal conditions, the proposed biosensor exhibits ultrahigh sensitivity toward target pathogenic bacteria with detection limits of 80 cfu mL−1. Besides, our biosensor also shows high selectivity toward target pathogenic bacteria and has the advantages in its low cost, simplified operations without the need of labeling steps and additional labile reagents. Hence, the EXPAR coupled DNAzyme amplification-based colorimetric method might create a useful and practical platform for detecting pathogenic bacteria and related food safety analysis and environmental monitoring.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...