Auto-accelerating and auto-inhibiting phenomena in the oxidation process of organic contaminants by permanganate and manganese dioxide under acidic conditions: effects of manganese intermediates/products†
Abstract
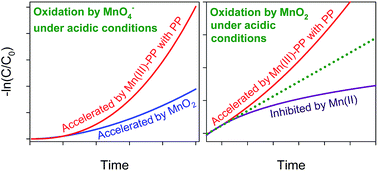
Considering the confused/controversial kinetics law of organic contaminant oxidation by permanganate (MnO4−) and manganese dioxide (MnO2) under acidic conditions, this study was conducted to systematically investigate the oxidation kinetics and mechanisms of contaminants by MnO4− and MnO2 under acidic conditions. The process of phenol oxidation by MnO4− showed an auto-accelerating trend at pH 2.0–6.0, which was mainly associated with the generation of MnO2, an oxidant more active than MnO4− under acidic conditions. However, an auto-inhibiting trend was observed during phenol oxidation by MnO2, which could be ascribed to the generation of Mn(II) and its subsequent adsorption on the surface of MnO2. The presence of excessive pyrophosphate (PP) greatly accelerated the oxidation of phenol by MnO4− and MnO2 under acidic conditions due to the generation and accumulation of highly reactive Mn(III)–PP. The presence of PP also changed the manganese species at equilibrium from MnO2 and Mn(II) to Mn(III)–PP, respectively, in the processes of organic contaminant oxidation by MnO4− and MnO2. In short, the reduction products of MnO4− and MnO2 determined the auto-accelerating or auto-inhibiting phenomenon observed in the process of phenol oxidation by MnO4− and MnO2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...