PdSn nanocatalysts supported on carbon nanotubes synthesized in deep eutectic solvents with high activity for formic acid electrooxidation
Abstract
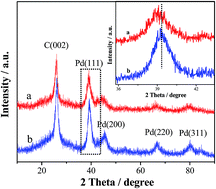
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are being increasingly used in electrochemically controllable synthesis of functional nanomaterials because of their unique merits (e.g., high conductivity, wide electrochemical windows and environmental friendship). Herein, we report a novel strategy in DESs for the fabrication of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)-supported Pd-based alloy nanostructures. Using a NaBH4 solvothermal reduction process in DESs, highly active PdSn alloy nanocatalysts supported on MWCNTs towards the formic acid oxidation (FAO) reaction were synthesized for the first time. The as-synthesized materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and electrochemical tests. The results demonstrate that the PdSn nanocluster structure with a rough surface provides a high density of catalytically active sites and thereby increases the electrochemically active surface area. There is a strong charge transfer interaction between Pd and Sn in the PdSn/MWCNT catalyst due to its high degree of alloying. The electrochemical studies indicate that the PdSn/MWCNT shows remarkably improved electrocatalytic performance towards FAO compared to Pd/MWCNT and commercial Pd/C catalysts. This study suggests an effective synthesis strategy for Pd-based electrocatalysts with high performance for DFAFCs applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...