A nitrogen and sulphur functionalized graphene oxide–palladium nanoparticle hybrid catalyst for an efficient Heck coupling†
Abstract
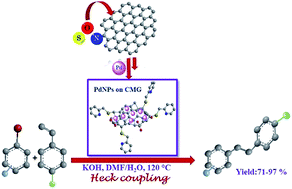
A nanocomposite comprised of Pd nanoparticles supported on chemically modified graphene (CMG) has been fabricated. Morphological and chemical characterization of the CMG–PdNP heterostructure has been carried out using PXRD, FTIR, Raman, XPS, TEM, SEM, EDX, and ICP-MS studies. The material contains 25.93 wt% of Pd(0) nanoparticles, with a diameter of 10–20 nm, well-dispersed on highly reduced graphene oxide containing a C/O ratio of 5.48. The efficacy of the CMG–PdNP system as a catalyst towards Heck cross-coupling with a variety of functionalized substrates has been demonstrated. Functionalization of reduced graphene oxide with heteroatoms like sulfur and nitrogen enhanced its dispersibility in organic solvents, and helped in stabilizing the active palladium species by acting as a ligand. The CMG–Pd composite exhibited an excellent catalytic activity with a substantially low catalytic loading (0.02 mol%), and the activity sustainable up to three reaction cycles. The remarkable effect might be a manifestation of N and S coordination to Pd, facilitating a high degree of dispersion and stabilization of Pd NPs onto the graphene surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...