Epitaxial growth and metallicity of rutile MoO2 thin film
Abstract
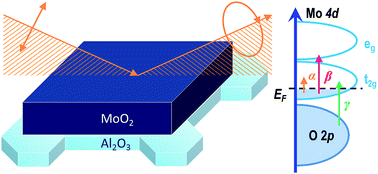
Molybdenum oxides have various crystal structures and physical properties due to the multiple valence states of the 4d molybdenum. Among them, MoO2 has a distorted rutile structure with chemical stability and metallic behavior. In this study we grew epitaxial (100) MoO2 thin films on (0001) Al2O3 substrates. Through careful control of the Ar-partial pressure and growth temperature, we determined the optimal growth condition. From our structural assessments, MoO2 epitaxial thin films with high crystallinity can only be achieved in very narrow growth conditions such as 500 °C and 7 mTorr. The thin film prepared under optimal condition showed good metallic behavior, which was confirmed by electronic transport and optical reflectance measurements. A detailed electronic structure was also investigated by spectroscopic ellipsometry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...