Synthesis, magnetism, aqueous-two phase formation and physical properties of novel guanidinium-based magnetic ionic liquids†
Abstract
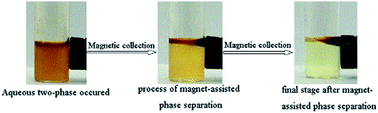
Magnetic ionic liquids (MILs) are a new class of ionic liquids that reveal paramagnetic properties. In this study, a series of novel guanidinium-based organic magnetic ionic liquids were synthesized and characterized by FT-IR and ESI-MS. The magnetic properties of these MILs were investigated using a vibrating sample magnetometer. With decreasing length of the carbon chain of the MILs, magnetic susceptibility was observed to strengthen. MILs also showed extremely strong paramagnetism when the temperature dropped below 25 K. A new concept of a magnetic ionic liquid aqueous-two phase system (MILATPs) was proposed for the first time. Compared to the latest developments in separation systems, the advantages of magnetic separation, organic solvent free and rapid extraction were successfully combined together in the novel proposed MILATPs. Interestingly, all these novel compounds are capable of forming MILATPs and can respond to an external magnetic field to accelerate isolation of two phases. In addition, some physical properties such as density, electrical conductivity and acidity were further studied. These MILs are expected to show great potential for further application in the fields of catalysis, desulfurization, biotechnology, electrochemistry, and especially separation and pretreatment technology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...