Carbon dioxide absorption in aqueous solution of potassium glycinate + 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol as new absorbents
Abstract
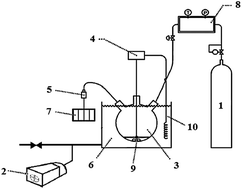
Aqueous solutions of potassium glycinate and mixtures with 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) are investigated as new absorbents for carbon dioxide absorption. The equilibrium solubility of carbon dioxide in the aforementioned aqueous solutions are measured for 0.01, 0.04 and 0.1 overall mass fractions, pressure range of 2.9–1382.4 kPa and temperature range of 293.15–323.15 K. Results show that carbon dioxide loading capacity has an inverse relation with temperature and solution concentration and the highest loading occurs at low concentrations of potassium glycinate. The extended Deshmukh–Mather model is used to predict the experimental data. The values of mean square error (MSE), average relative deviation (ARD) and correlation coefficient (R2) for the extended Deshmukh–Mather model are 0.0576, 9.0561 and 0.9859, respectively. In addition, an artificial neural network (ANN) is also developed to estimate CO2 loading in the studied solutions. Results show there are good agreements between experimental data and predicted values. The values of MSE, ARD and R2 for the optimal trained ANN are 0.0256, 5.4290 and 0.9946, respectively. From an economic perspective and stability considerations in the presence of O2, a 1.0% wt potassium glycinate + 3.0% wt AMP blend, is considered optimal.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...