Rhodium-doped titania photocatalysts with two-step bandgap excitation by visible light—influence of the dopant concentration on photosensitization efficiency†
Abstract
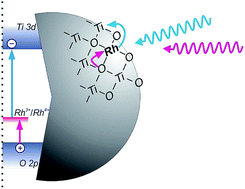
Development of photocatalysts active under visible light has been achieved through the modification of titania with rhodium (Rh) ions. Depending on the concentration of the precursor of Rh species, various crystalline phases and modification modes have been obtained. Lower Rh concentrations (below 0.5%) resulted in doped rutile particles, while higher (above 1%) gave mainly surface modified anatase particles. High photocatalytic activities were obtained for surface enriched doped rutile-titania with an extremely low amount of trivalent rhodium (Rh3+) ions (about 0.0005 mol%). Almost four orders of magnitude higher Rh concentration (2%) also provided highly active materials, however, they were composed of mainly anatase particles with photoactive surface RhOx species. Extremely low Rh concentration allowed to limit the amount of intrinsically present tetravalent rhodium (Rh4+) species, which may decrease charge mobility in the titania lattice and promote the recombination route in Rh-doped materials. Photoactive Rh species created in low concentrated samples were able to drive reversible redox processes controlled by the range of light energies. Photocatalytic activity tests, action spectra and photoelectrochemical measurements allowed to propose a unique photosensitization mechanism, involving an Rh3+/Rh4+ redox couple acting as built-in redox mediator, in which both electrons in the conduction band (CB) and positive holes in the valence band (VB) might be generated upon irradiation with visible light. Such a mechanism was not valid for materials containing higher amounts of Rh composed of mainly anatase. Detailed studies on the properties of the materials containing various amounts of Rh species (0.0001–3 mol%) showed the dependency of efficiency of photoinduced processes on Rh concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...