Enhanced CO2 adsorption on Al-MIL-53 by introducing hydroxyl groups into the framework†
Abstract
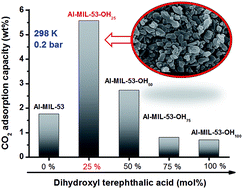
A series of hydroxyl functionalized Al-MIL-53 materials (Al-MIL-53-OHx) containing varying hydroxyl molar ratios (x = 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100%) were synthesized via a mixed-linker approach, wherein x denotes the molar ratio of 2,5-dihydroxy terephthalic acid:(2,5-dihydroxy terephthalic acid + terephthalic acid). All Al-MIL-53-OHs exhibited an identical structure to that of Al-MIL-53. The thermal stability of Al-MIL-53 decreased after introducing hydroxyl groups. The hydroxyl functionalized Al-MIL-53 containing 25 mol% and 50 mol% of hydroxyl group showed higher surface areas (SBET = 1270 and 1260 m2 g−1 for Al-MIL-53-OH25 and Al-MIL-53-OH50, respectively) than that of Al-MIL-53 (SBET = 819 m2 g−1). A further increase in the OH groups (75 mol% and 100 mol%) led to dramatical compromise of the framework. The presence of hydroxyl groups affected not only the CO2 adsorption capability but also the ‘breathing effect’ of MIL-53 resulting from the intraframework interaction. The CO2 adsorption capacities of Al-MIL-53-OH25 and Al-MIL-53-OH50 at 1 bar at 25 °C were 8.5 and 8.3 wt%, respectively, which are about 19% higher than that of Al-MIL-53 under the identical conditions. Moreover, pronounced improvement in CO2 adsorption was observed below 0.2 bar, especially for Al-MIL-53-OH25 (5.5 wt% for Al-MIL-53-OH25 vs. 1.7 wt% for Al-MIL-53). This behavior is due likely to the enhanced isosteric heat of CO2 adsorption. The hydroxyl group plays a positive role in the CO2 adsorption performance of Al-MIL-53, which is comparable to amino groups. Al-MIL-53-OHx (x = 75 and 100) displayed lower CO2 adsorption capacities despite the higher isosteric heat of CO2 adsorption, which might be due to the blocked pores in the presence of dense hydroxyl groups.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...