Improving detection sensitivity by oriented bioconjugation of antibodies to quantum dots with a flexible spacer arm for immunoassay
Abstract
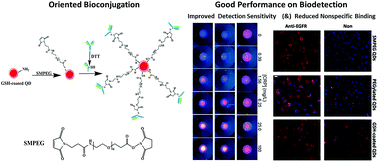
Antibodies with high targeting capability after being labelled by quantum dots (QDs) have been of great importance for in vitro diagnostic, cellular imaging and in vivo theranostic applications. However, such work concentrating on the conjugation of QDs and antibodies is still insufficient. It is encouraged to develop reliable bioconjugation strategies to improve detection sensitivity of QD–antibody bioconjugates. In this study, two bioconjugation approaches were used for antibody and QDs covalent coupling. Their detection sensitivity was parallelly determined and compared. It was experimentally found that succinimidyl valerate-PEG-maleimide (SMPEG) as the cross linker for oriented bioconjugation of antibodies to QDs with a flexible spacer arm can significantly improve the detection sensitivity of the resulting QD–antibody bioconjugates, compared with those prepared with traditional carbodiimide chemistry using EDC·HCl as the cross linker. Gel electrophoresis suggests antibodies can be successfully conjugated with QDs by both the EDC method and the SMPEG method, but immunofiltration assay shows QD–antibody bioconjugates obtained by the SMPEG strategy have lower detection limits and better linear scope patterns for in vitro molecular diagnosis. In vitro cancer cell imaging further shows that QD–antibody bioconjugates prepared by the SMPEG strategy have superior cell targeting capability without observable nonspecific binding, while the EDC-mediated QD–antibody bioconjugates have low signal to noise ratios with obvious nonspecific cellular binding. Moreover, the number of antibodies conjugated on the surface of QDs was determined by the chemiluminescent dot blot assay, showing 2.13 ± 0.5 and 0.76 ± 0.2 of antibodies per QD by EDC-mediated and SMPEG-mediated coupling, respectively. It further verifies that the SMPEG-mediated coupling strategy can significantly maintain the biological activity of the linked antibodies, even though it has low labelling efficiency. It could be therefore claimed that oriented bioconjugation via the SMPEG coupling strategy is favored by immunoassays, with improved detection sensitivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...