Discovery of a novel oxime ether scaffold as potent and orally bioavailable free fatty acid receptor 1 agonists†
Abstract
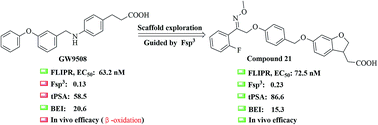
The free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA1) plays a key role in amplifying glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells. Most of the reported FFA1 agonists contain a biphenyl scaffold, which is associated with toxicity as verified by Daiichi Sankyo. Herein, we describe the systematic exploration of a non-biphenyl scaffold to improve the druggability of GW9508 (β-oxidation, Fsp3 = 0.13, tPSA = 58.5 Å2) directed by Fsp3 and tPSA values. All these optimizations ultimately led to the identification of compound 21, an unconventional agonist (EC50 = 72.5 nM) bearing a methyl oxime ether scaffold. Moreover, compound 21 revealed improved drug-like properties (Fsp3 = 0.23, tPSA = 86.6 Å2) when compared to GW9508 (Fsp3 = 0.13, tPSA = 58.5 Å2) and an even higher binding efficiency index (BEI = 15.3) than TAK-875 (BEI = 14.3). Further pharmacological studies suggested that compound 21 has a considerable hypoglycemic effect in both normal and type 2 diabetic mice with a low risk of hypoglycemia. In addition, the docking study promoted our understanding of the ligand-binding pocket. This information might help towards the design of more promising new molecular entities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...