Efficient, robust surface functionalization and stabilization of gold nanorods with quaternary ammonium-containing ionomers as multidentate macromolecular ligands†
Abstract
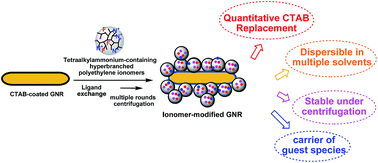
Surface functionalization of gold nanorods (GNRs) is critical to their applications in various fields. While there are several existing strategies, we report in this article a new general strategy for the surface functionalization of GNRs with quaternary ammonium-containing ionomers as a novel class of multidentate macromolecular surface ligands. A range of tetraalkylammonium-containing hyperbranched polyethylene- and linear poly(n-butyl acrylate)-based ionomers has been specifically designed and employed in the strategy. Acting as multidentate macromolecular analogues of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), the ionomers have been demonstrated to bind onto the GNR surface by displacing the surface-bound CTAB species via ligand exchange to render CTAB-free ionomer-modified GNRs. By properly designing the enabling ionomers, we have shown that the modified GNRs can be endowed with some desired properties, such as excellent dispersibility in various organic solvents, robust stability under multiple rounds (up to 12 investigated) of high-speed centrifugation in organic solvents, amphiphilicity with dispersibility in both aqueous and organic media, fluorescence, and capability in carrying hydrophobic guest species. This strategy thus provides potential new ways for the construction of novel multifunctional GNR nanocomposites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...