Cuprous oxide/titanium dioxide nanotube-array with coaxial heterogeneous structure synthesized by multiple-cycle chemical adsorption plus reduction method
Abstract
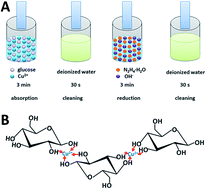
We report the formation and characterization of a cuprous oxide/titanium dioxide (Cu2O/TiO2) nanotube-array coaxial heterogeneous structure, which is supposed to have potential applications in photo-induced water decomposition and organic pollutant degradation. Such structure is formed by coating nano-particles of Cu2O onto titanium dioxide nanotube-array walls via multiple-cycle chemical adsorption plus reduction method (MC-CAR). The practical deposition technique employs a soaking step to separate the adsorption and reduction processes, thus enhancing the controllability of deposition rate and preventing the clogging of nanotube pores. The size of Cu2O nano-particles is adjusted by changing the glucose concentration in the reaction solutions. As a result, compact nano-particle film with sufficiently small crystal sizes is uniformly covered on the tube walls, resulting in the formation of coaxial heterogeneous structure. The detailed synthesis process and the surface morphology, structure, photoelectric properties, and hydrogen evolution ability of the Cu2O/TiO2 nanotube-array with coaxial heterogeneous structure are systematically investigated. The resulting film shows a stable hydrogen production rate of 3.1 mL cm−2 h−1, which can be targeted for energy application in relation with solar energy driven production of hydrogen from water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...