Enhanced electrochemical performance of phosphorus incorporated carbon nanofibers by the spin-on dopant method†
Abstract
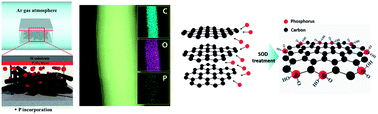
Phosphorus-incorporated carbon nanofibers (CNFs) were successfully fabricated by using electrospinning and spin-on dopant (SOD) procedures together for electrochemical capacitors (ECs). Microstructural and chemical investigations indicated that phosphorus was uniformly incorporated into the CNFs without any impurities or alloys by using an SOD treatment. The specific surface area of the SOD-treated CNFs increased by over 1.47 times when compared to that of conventional CNFs due to an increase in the total pore volume. In addition, the SOD-treated CNFs contained many beneficial functional groups such as phosphate and hydroxyl groups. ECs, fabricated from SOD-treated CNFs as electrodes, showed enhanced electrochemical performance such as high capacitance (up to 188 F g−1), good high-rate performance with a capacitance retention of 84%, an excellent energy density (17.2–23.5 W h kg−1 in a power density ranging from 360 to 4680 W kg−1), and an excellent cycle stability (86% up to 1000 cycles). These enhancements were attributed to the beneficial effects of the SOD method applied to the CNFs to enlarge the surface area and provide many functional groups.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...