Improved H2 uptake capacity of transition metal doped benzene by boron substitution
Abstract
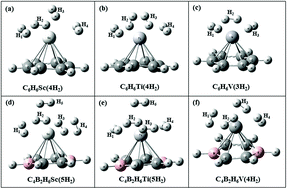
The effect of boron substitution on hydrogen storage capacity of transition metal (TM) doped benzene is studied using density functional theory and the second order Møller–Plesset method with aug-cc-pVDZ basis set. Out of the six carbon atoms in a benzene ring, two are substituted by boron atoms. The structures considered here are C4B2H6TM (TM = Sc, Ti, V). Four, four and three H2 molecules can be adsorbed on unsubstituted C6H6Sc, C6H6Ti and C6H6V complexes, respectively, whereas upon boron substitution one additional H2 molecule gets adsorbed on each of these complexes. The H2 uptake capacity of C4B2H6Sc, C4B2H6Ti and C4B2H6V obtained is 7.71, 7.54 and 5.99 wt%, respectively. Gibbs free energy corrected adsorption energies show that H2 adsorption on C4B2H6Sc is energetically unfavorable whereas it is favorable on C4B2H6Ti and C4B2H6V at ambient conditions. Various interaction energies for the H2 adsorbed complexes are obtained using a many-body analysis technique. The H2 desorption temperature for boron substituted TM doped benzene is lower than that for TM doped benzene for all the three systems. Molecular dynamics simulations show that loosely bonded H2 molecules in C4B2H6Sc(5H2) and C4B2H6Ti(5H2) complexes fly away during the simulation, thereby showing lower H2 uptake capacity of these complexes than that obtained by electronic structure calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...