Bi doped CeO2 oxide supported gold nanoparticle catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols†
Abstract
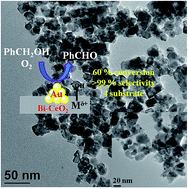
Gold nanoparticles supported on Bi–CeO2 with four different bismuth loadings (2 to 8 mol%) were prepared to determine the role of oxide vacancies in doped ceria in the benzyl alcohol oxidation reaction. The catalytic activity was tested for a liquid phase benzyl alcohol oxidation reaction with molecular oxygen under mild conditions of pressure and temperature. The catalytic activity depends on the optimum composition of bismuth concentration (2 to 8 mol%), the nominal gold loading (1 to 4 wt%) and the preparation method of the gold nanoparticles (DP-NaOH, or DP-Na2CO3, gold concentration, and calcination temperature). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) results showed that Au(3.5 wt%)/Bi(6 mol%)–CeO2 catalyst had the smallest Au NPs, and the majority of Au particles had diameters in the range of 4.04 ± 0.8 nm. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) revealed both metallic and oxidized gold species on the surface of Bi–CeO2. Au(3.5 wt%)/Bi(6 mol%)–CeO2 catalyst showed superior activity for the oxidation reaction of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde (conversion 60% and >99% selectivity). The catalysts exhibited a high turnover frequency (TOF) value (0.144 s−1) for benzyl alcohol oxidation. The strong metal support interactions occur due to the presence of higher amounts of positively charged gold species, and a higher number of surface oxygen vacancy sites was responsible for the high catalytic activity of the Au(3.5 wt%)/Bi(6 mol%)–CeO2 catalyst. Corresponding kinetic measurements indicated that the reaction has an apparent activation energy of 34.1 kJ mol−1. Microkinetic studies showed that there was no mass transfer limitation in the three phase catalytic system. The catalyst exhibited high TOFs for the oxidation of other alcohols, such as 2-octanol, cinnamyl alcohol and geraniol, under similar reaction conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...