Numerical simulation of hot-spot effects in microwave heating due to the existence of strong microwave-absorbing media
Abstract
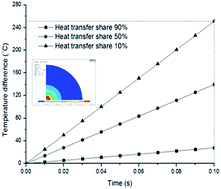
Hot spots can occur in microwave heating when the heated materials have different microwave absorbing properties, resulting in non-uniform temperature distribution. Understanding the features and extent of hot-spot effects can be essential in microwave-assisted processes, but little has been reported quantitatively due to the difficulty in direct determination. The issues are measured experimentally and numerically simulated using silicon carbide (SiC) particles dispersed in paraffin oil as a representative case here. Hot spots are definitively shown to exist and may trigger temperature gaps between surrounding substances at the magnitude of several hundred degrees Celsius or even higher in certain cases. The temperature gaps are enhanced for larger sized SiC particles, with a higher heat generation rate and increasing heating time. The extent of hot-spot effects substantially depends on how much and how quickly heat generated by the strong microwave absorbing media can be transferred to the weak ones. The findings have great practical value. By choosing materials with strong microwave absorption, or where discharges occur due to microwave–metal interactions, prominent hot spots can be intentionally forged and the temperature gradient may be tailored to enhance chemical reactions and catalytic processes for specific scientific and engineering applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...