Iron and nitrogen co-doped titania matrix supported Pt for enhanced oxygen reduction activity in polymer electrolyte fuel cells†
Abstract
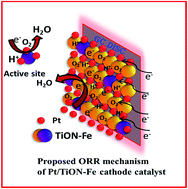
The catalytic activity of iron and nitrogen co-doped modified titania matrix as a stable support for platinum towards improved oxygen reduction reaction in polymer electrolyte fuel cell is studied. Electrochemical studies on oxygen reduction reaction are carried out by linear sweep voltammetry and show the optimum level of iron and nitrogen co-doped titania supported platinum (Pt/TiON–Fe 2) with increased oxygen reduction reaction activity. The formation of defect states, metal composition, doping effects, platinum interaction with Fe and N moieties, functional groups and chemical oxidation states are studied by X-ray diffraction, high resolution scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The optimum material (with levels of iron 1.5–2 wt% and nitrogen 8–10 wt% co-doped into the titania matrix) shows increased fuel cell performance at 60 °C with a metal (Pt) loading of 0.2 mg cm−2 as compared to Pt/C. Besides, the effects of platinum loading and relative humidity are examined using optimized electrocatalysts. Pt/TiON–Fe 2 has shown higher corrosion resistance up to 1.5 V and also exhibits a peak power density of 900 mW cm−2 with a Pt loading of 0.15 mg cm−2 at 3 bar back pressure. Pt/TiON–Fe 2 retains 88% ECSA even after 10 000 potential cycles of an accelerated durability test.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...