SPIO@SiO2–Re@PEG nanoparticles as magneto-optical dual probes and sensitizers for photodynamic therapy†
Abstract
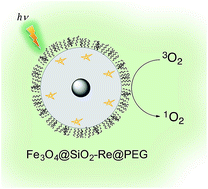
A dual magneto-optical nanoprobe, endowed with properties useful for photodynamic therapy, has been prepared. It is constituted by a superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) core (diameter size distribution centered at ca. 10 nm), obtained by thermal decomposition of iron oleate, coated by a compact silica shell, grown in a reverse microemulsion environment. Luminescent [Re(phen)(CO)3(py)]CF3SO3 complexes were covalently anchored to the silica shell, by functionalizing the pyridine ligand with a triethoxysilane moiety. Finally, the surface of the nanoparticles (NPs) was coated with a layer of polyethylene glycol (PEG), functionalized with triethoxysilane, to improve stability and stealthiness in physiological conditions. Transmission electron microscopy of these SPIO@SiO2–Re@PEG nanocomposites showed a single population, with size distribution centered at ca. 40 nm. NPs showed nuclear relaxivity values that guarantee an appreciable contrast in magnetic resonance imaging (r2 > 30 s−1 mM−1 at frequencies higher than 5 MHz). The presence of the Re complexes imparted photoluminescence to the NPs, with blue shifted emission and higher photoluminescence quantum yields with respect to the free [Re(phen)(CO)3(py-upts)]+ complex (λem 553 vs. 580 nm, Φ 0.060 vs. 0.038, in aerated water solution). The complexes embedded into the NPs maintained a satisfactory efficiency toward 1O2 generation (quantum yields 0.21 vs. 0.26 for the free complex, as assessed using 1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene as indirect marker of the 1O2 presence). Preliminary cell penetration tests were performed on human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Two photon excitation confocal microscopy showed that the NPs were easily internalized and accumulated in the perinuclear region of the cells already after 4 h of incubation. Increased cytotoxicity upon irradiation with respect to the dark was also observed, showing the potential of the nanocomposite for photodynamic therapy applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...