Aggregation and surface behavior of aqueous solutions of cis-bis(1,3-diaminopropane)bis(dodecylamine)cobalt(iii) nitrate. A double-chained metallosurfactant†
Abstract
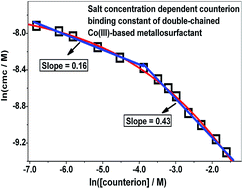
Metallosurfactants or amphiphilic metal complexes are emerging as a new class of material with a range of properties inherent to both metal complexes and surfactants. Looking at the potential applications of these materials in diverse fields, studying the fundamental aspects of their adsorption and aggregation is necessary. cis-Bis(1,3-diaminopropane)bis(dodecylamine)cobalt(III) nitrate (DDCN), a double-chained cationic metallosurfactant, was synthesized and its critical micelle concentration values were determined in aqueous medium as a function of sodium nitrate concentration by using surface tension, conductivity and spectrophotometric methods. Thermal gravimetric analysis showed stability of DDCN up to about 183 °C. DDCN has a salt dependent counterion binding constant, a low value equal to 0.16 becomes more than double (0.43) above 0.025 mol kg−1 NaNO3. The counterion binding constant value of DDCN is however surprisingly low compared to other ionic surfactants. Dynamic light scattering measurements revealed large size aggregates (hydrodynamic diameter = 116 nm with polydispersity index = 0.23) of DDCN which grow even larger on adding NaNO3. Small angle neutron scattering measurements also showed the presence of large size DDCN aggregates existing probably as micellar clusters. Adsorption behavior of DDCN was assessed by calculating surface excess and area per molecule at the air/water interface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...