Enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of electrodeposited hematite films decorated with nanostructured NiMnOx
Abstract
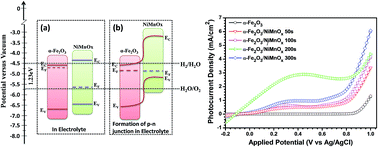
In the present work, we report a novel nickel-manganese oxide (NiMnOx) decorated hematite (α-Fe2O3) photoanode for efficient water splitting in a photoelectrochemical (PEC) cell. The photoanodes are prepared by a two step electrodeposition process. NiMnOx loading on the hematite surface is varied by changing the electrodeposition time. The NiMnOx loaded α-Fe2O3 photoanodes are characterized by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, UV-Vis absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy. The results demonstrate that the NiMnOx decorated α-Fe2O3 photoanode exhibits excellent photoelectrochemical activity. The α-Fe2O3/NiMnOx photoanode, where NiMnOx was coated for 200 s, shows a maximum photocurrent of 2.35 mA cm−2 at an applied potential of 0.23 V vs. the Ag/AgCl reference electrode. There is a large shift in the onset potential towards the cathodic region also observed. The photoconversion efficiency is calculated which is around 0.85% at 0.23 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The superior PEC performance of NiMnOx decorated α-Fe2O3 photoanodes can be explained by a combined effect of better water oxidation on the hematite surface and efficient separation of photogenerated electron–hole pairs on its surface due to NiMnOx modification.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...