Development of functionalized quantum dot modified poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes for fuel cell applications
Abstract
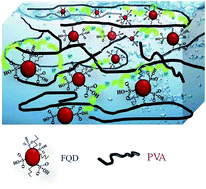
This paper describes the preparation and characterization of membranes based on poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) cross-linked using functionalized CdSe quantum dots [FQDs] (size 4 ± 0.2 nm). FQDs having –COOH and –SO3H functionalities on the surface were synthesized by the ligand exchange method using a mixture of 3-mercaptopropionic acid and 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid. Both sulfonic (–SO3H) and carboxylic (–COOH) groups are expected to enhance the dimensional/thermal stability of PVA [by cross-linking] and proton conductivity [as proton donors]. Several membranes were prepared by mixing an aqueous solution of PVA with varying amounts of FQDs and then cross-linked by thermal treatment. Cross-linked membranes were characterized for structural (FTIR-ATR) and thermal behaviour (TGA, DSC, DMA), morphology (SEM, TEM, XRD), water uptake and proton conductivity. Hydrolytic stability and Tg increased with increasing degree of cross-linking. All of the cross-linked membranes had proton conductivity of 10−3 S cm−1 in the temperature range of 25 °C to 70 °C at 100% relative humidity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...