Zwitterionic buffer-induced visible light excitation of TiO2 for efficient pollutant photodegradation†
Abstract
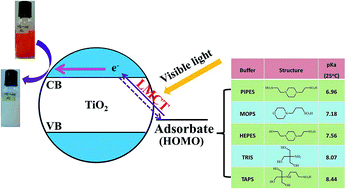
Excitation of TiO2 for visible light absorption by surface complexation with antenna organic molecules is an effective strategy to improve its solar utilization efficiency for photocatalytic application, but the existing antenna molecules are mostly toxic and environmentally-aggressive, severely limiting their practical application. In this study, we tested the potential of zwitterionic buffers (Good's buffers) as an environmentally-benign alternative. The addition of Good's buffers significantly enhanced methyl orange (MO) photodegradation by TiO2 under visible light, but the enhancement degree varied with the different buffer types, buffer concentration and solution pH. The presence of 4-(2-hydroxyerhyl) piperazine-1-erhanesulfonic acid (HEPES) as a typical Good's buffer led to over 90% MO removal within 180 min, whereas only slight MO removal was observed in the TiO2 alone system during the same period. Such an induced visible light photocatalytic activity was attributed to a complexation between the conjugate acid structured buffer molecule and TiO2, which favors a ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT). The LMCT activity was strongly dependent on the molecule structure, especially the states of hydroxyl and amino groups of Good's buffers. The pH buffering ability of the buffers also contributed to the efficient MO photodegradation. This study suggests a great potential of Good's buffers as both “green” antenna molecules and pH buffer for strengthening TiO2-based photocatalytic remediation processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...