Hybrid LiV3O8/carbon encapsulated Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2 with improved electrochemical properties for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
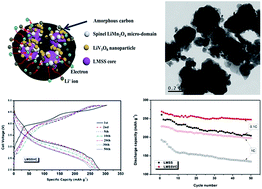
A low coulombic efficiency in the first cycle and poor rate capability limit the practical application of a lithium rich manganese-based solid solution (LMSS) in lithium ion batteries. To resolve these problems, a core–shell type of Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2@LiV3O8/C (LMSSVC) composite material was prepared using a sol–gel process, in which NH4VO3-derived V2O5 chemically leached lithium from the LMSS and formed the LiV3O8 during high temperature annealing. The effect of the hybrid LiV3O8/C layer on the electrochemical properties of the LMSS is investigated using cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and galvanostatic charge–discharge measurements. The as-prepared LiV3O8 nanoparticles are embedded within the carbon matrix uniformly, which becomes an outer shell to encapsulate the LMSS nanoparticles. Because of the Li-host nature of LiV3O8 and the electronic conductivity of carbon, the LMSSVC can deliver a capacity of 269 mA h g−1 at a 0.1C rate in the first cycle over the voltage range of 2.0–4.8 V together with a coulombic efficiency of 94%, and retain 94% of the initial capacity after 50 cycles. It can deliver capacities of 258, 245, 229, 207 and 176 mA h g−1 at the rates of 0.2C, 0.5C, 1C, 2C and 5C, respectively. The results indicate that surface coating of the hybrid LiV3O8/C layer can improve not only the initial coulombic efficiency but also the rate capability of the LMSS material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...