Long-term and oxidative-responsive alginate–deferoxamine conjugates with a low toxicity for iron overload
Abstract
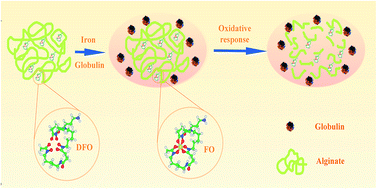
To address the drawbacks of deferoxamine, a clinical drug widely used for iron-overload-related conditions, oxidation-responsive alginate–deferoxamine (Alg–DFO) conjugates were prepared and their structure characterized by size-exclusion chromatography, FTIR, and 1H NMR. The prepared conjugates exhibited long-term stability, with a half-life 9.8–17.8 times longer than that of the free DFO, depending on the molecular weight of the conjugated alginate. On the other hand, the conjugates could quickly respond to oxidative stimuli and be degraded, which suggests they hold the potential to be cleared from the body in an iron-overload-related oxidative environment to avoid their accumulation and to address safety concerns. The degradation mechanism for the oxidative response is proposed. At the same time, it is interesting to find that the conjugates are capable of protecting the iron-binding capacity of the attached DFO from the oxidation environment, which probably is a result of the antioxidant activities of the conjugated alginate. In addition, the conjugates show a lower cytotoxicity in comparison with the free DFO. Overall, it is anticipated that the Alg–DFO conjugates prepared in this work will have the potential to be used for treating iron-overload-related disease.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...