Identification and characterization of stressed degradation products of rabeprazole using LC-ESI/MS/MS and 1H-NMR experiments: in vitro toxicity evaluation of major degradation products†
Abstract
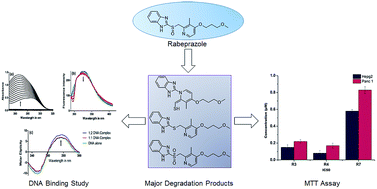
Rabeprazole, an antiulcer drug in the class of proton pump inhibitors was subjected to force degradation studies as per ICH guidelines Q1A (R2). The chromatographic separation of the drug and its degradation products were achieved on a Purospher STAR, C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μ) using 10 mM ammonium acetate (pH-7.0): acetonitrile as a mobile phase in gradient elution mode at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1. A total of 10 (R1–R10) hitherto unknown degradation products were identified and characterised by LC-ESI-MS/MS experiments and accurate mass measurements. The most probable mechanisms for the formation of DPs have been proposed based on a comparison of the fragmentation of the [M + H]+ ions of rabeprazole and its degradation products. Major degradation products (R3, R4 and R7) were isolated by semi preparative HPLC using Water's X-bridge Prep C18 (250 × 10 mm, 5 μ). In vitro toxicity evaluation of the isolated degradation products showed more than 50% cell inhibition at concentrations of less than 1 μM on HepG2 cell and PANC-1 cell lines. DNA binding studies using spectroscopic techniques indicate that the R3, R4 and R7 ligand molecules bind to the surface of double stranded DNA and stabilize the DNA complex.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...