Reductive dehalogenation of brominated disinfection byproducts by iron based bimetallic systems†
Abstract
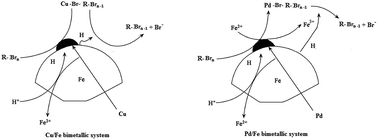
The reductive dehalogenation of brominated disinfection byproducts (DBPs) including bromoform and tribromoacetic acid (TBAA) by iron based bimetallic systems (Cu/Fe and Pd/Fe) was investigated. In Cu/Fe bimetallic system, only 8.1% of bromoform and 20.1% of TBAA were reduced within 20 min when the particle dosage was 5 g L−1, while 56.9% of bromoform and 62.7% of TBAA were removed in the same period when the dosage increased to 20 g L−1. A complete removal of bromoform and TBAA was achieved within 60 min of reaction in acidic conditions, while only 35.4% of bromoform and 10.8% of TBAA were removed after the whole experimental period (140 min) in alkaline conditions. Similar results were observed in a Pd/Fe bimetallic system. Bimetallic particles achieved high performance probably because galvanic cells were created between Fe (serving as an anode) and plating elements (serving as a cathode). This structure enhanced the reducibility of iron for reductive dehalogenation by facilitating iron corrosion as well as reducing the activation barrier of H2. The Pd/Fe system showed a better performance than Cu/Fe, which was attributed to a higher potential gradient (1.4 V) as compared to Cu/Fe couples (0.8 V). Furthermore, toxic assessment indicated that the toxicity of water samples had a dramatic decline after dehalogenation by bimetallic particles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...