In situ synthesis of a bio-cellulose/titanium dioxide nanocomposite by using a cell-free system
Abstract
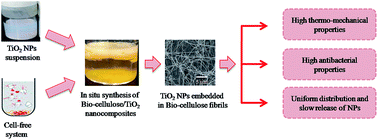
In the current study, nanocomposites of bio-cellulose with titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2-NPs) were synthesized by an in situ strategy using a cell-free system. The system was developed from Gluconacetobacter hansenii PJK through bead beating. A suspension of TiO2-NPs was prepared in 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate and added to the cell-free extract of G. hansenii PJK. The bio-cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite was synthesized at 30 °C, pH 5.0 for 5 days (bio-cellulose/TiO2-I), 10 days (bio-cellulose/TiO2-II), and 15 days (bio-cellulose/TiO2-III) using 10 g L−1 glucose. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) confirmed the structural features and impregnation of TiO2-NPs into the bio-cellulose matrix. Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy confirmed the presence of Ti–O groups in the chemical structure of the nanocomposite. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis indicated the presence of specific peaks for bio-cellulose and TiO2-NPs in the nanocomposite. The TiO2-NP uptake by bio-cellulose was greatly increased with time and 40 ± 1.6% of the initially added nanoparticles were successfully impregnated into the nanocomposite after 15 days of incubation. NP release analysis revealed minute detachment though a prolonged treatment time of 10 days. The synthesized nanocomposite showed better thermal and mechanical properties compared to pure bio-cellulose. The antibacterial test revealed impressive results where the inhibition zones produced against E. coli by bio-cellulose, bio-cellulose/TiO2-I, bio-cellulose/TiO2-II, and bio-cellulose/TiO2-III were zero, 2.1 cm, 2.5 cm, and 3.7 cm, respectively. The current strategy can be effectively employed for the development of composite materials of biopolymers with several kinds of bactericidal elements.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...