Determination of riboflavin based on fluorescence quenching by graphene dispersions in polyethylene glycol†
Abstract
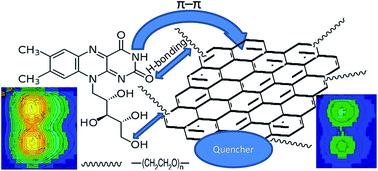
The effect of graphene (G) dispersions in a biodegradable polymer, polyethylene glycol (PEG), on the fluorescence emission of vitamin B2 (riboflavin) has been studied. The ultrasonication time and power used for the preparation of the dispersions have been optimized, and their quality has been evaluated by measuring the thickness of the G flakes and their distribution within the polymer by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and by determining their defect content and degree of exfoliation by Raman spectroscopy. A quenching phenomenon of riboflavin fluorescence has been observed, attributed to π–π stacking interactions between the aromatic rings of the vitamin and G combined with PEG-riboflavin H-bonding interactions. The analysis of the fluorescence spectra confirms that, for mild ultrasonication conditions, the quenching becomes more effective on increasing G concentration, whilst for more intense conditions it is almost independent on the nanomaterial loading. Moreover, for a given G concentration, the fluorescence intensity increases slightly at low PEG contents, while it remains almost constant at high concentrations. The ratio data between the fluorescence intensity in the absence and in the presence of G fit to a second-order polynomial equation, suggesting a combined mechanism of static and dynamic quenching. The analytical characteristics of the fluorimetric method have been calculated for PEG aqueous solutions, for G dispersions in PEG and for the differences of intensities between them, and the best results were obtained in the presence of G. The proposed method was successfully applied to the analysis of riboflavin in multivitamin tablets, and the recoveries found in fortified samples were higher than 90%. The quenching phenomenon observed in this work could be employed for the development of new optical sensors for riboflavin determination.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...