FTIR metabolomic fingerprint reveals different modes of action exerted by active pharmaceutical ingredient based ionic liquids (API-ILs) on Salmonella typhimurium†
Abstract
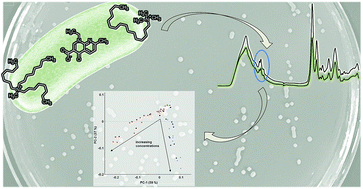
Since their incorporation into various chemical and biochemical processes, ionic liquids (ILs) have now been found useful for biomedical applications, including active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) such as antimicrobial agents or antibiotics. Recently, synergistic API-ILs with great potential have been reported, which show either increased antimicrobial activity or the ability to overcome bacterial resistance. In this study a total of 19 API-ILs, based on the antibiotic nalidixic acid, combined with different cation species, were investigated for synergistic effects against the important foodborne pathogen Salmonella. Furthermore, 19 respective ILs with chloride as the anion were used to control the effects of the different cation species. The antimicrobial activities of all 38 ILs against six different Salmonella species, as well as two nalidixic acid-resistant S. typhimurium strains, were determined via the microbroth dilution assay. The response pattern of the main cellular constituents, namely proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids of the bacterial cells to the most promising API-ILs was further investigated by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. While a number of active API-ILs based on nalidixic acid could be synthesized, no evidence for synergistic effects, such as increased antimicrobial activity or the ability to overcome resistance was found with either microbiological or spectroscopic methods. However, it could be demonstrated for the first time that while the different IL species ([TC8MA]+ and [TMC16A]+) showed similar antimicrobial activity, the FTIR spectral patterns indicated changes in bacterial membrane fluidity suggesting different modes of action.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...