Protein adsorption by a high-capacity cation-exchange membrane prepared via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization†
Abstract
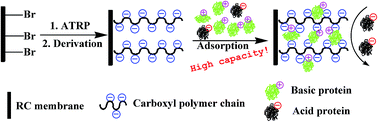
In this study, a weak cation-exchange (WCX) membrane was prepared via a “post-polymerization modification” method, which involved the surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) and subsequent two-step derivation. By varying the graft time of poly-GMA, a series of WCX membranes with different densities of carboxyl groups were fabricated. For the membrane with a graft time of 12 h, a high adsorption capacity of 125.0 mg mL−1 was obtained by using lysozme (Lys) as a model protein, which is higher than that reported. The new parameters, the utilization percentage of carboxyl (UP) and the stoichiometric displacement parameter (Z) were introduced to theoretically investigate how the ligand density affects the adsorption behavior of Lys for the first time. The UP revealed an “increase first and then decrease” trend with the prolonging of graft time, which may result from the mutual effect of the flexibility of the polymer chain, the steric hindrance and the “adsorption-caused hindrance” effect. Remarkably, the Z value was found to increase with the prolonging of graft time, suggesting that more effective binding sites were interacting with a protein molecule when the density of carboxyl was increased. Finally, the WCX membranes were applied to purify Lys from egg white with a high recovery of 95.7%, which depends significantly on the adsorption capacity of the membranes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...