Effect of particle size on the surface activity of TiC–Ni composite coating via the interfacial valence electron localization
Abstract
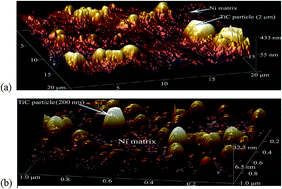
Electron work functions (EWF) and open potentials of electrodeposited nickel, TiC microparticle-reinforced and TiC nanoparticle-reinforced Ni matrix coatings were studied with the objective of investigating the effects of TiC particle size on the surface activity and corrosion tendency of the coatings. First-principles calculation was conducted to elucidate the underlying mechanism. Results of the study demonstrate that the overall EWF and open potential of Ni coating decreased when TiC microparticles (diameter = 2 μm) were added. However, TiC nanoparticles (diameter = 200 nm) showed opposite effects. Such changes are ascribed to the effect of particle size on the TiC/Ni interfacial state. It was shown that TiC microparticle/Ni interface had a low interfacial EWF. While the TiC nanoparticle resulted in a stronger TiC/Ni interface with elevated EWF. The first-principles calculation revealed that valence electrons were more localized in the region of the nano TiC/Ni interface, resulting in higher EWF, stronger interfacial bonding, and higher surface stability that limited the electrons available to participate in corrosion reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...