Polyethylenimine analogs for improved gene delivery: effect of the type of amino groups†
Abstract
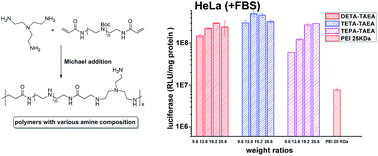
A significant gap currently exists in our understanding of how the detailed chemical characteristics of polycationic gene carriers can improve their delivery performance. The aim of this contribution is to develop a branched polyethylenimine (PEI)-mimetic biodegradable polymer that can increase the transfection efficiency (TE). Michael addition between tris(2-aminoethyl)amine and diacryl amides with special structures was applied to synthesize several degradable polymers with different amine compositions (primary/secondary/tertiary). The 1 : 1 polymerization could be confirmed by NMR, making the amine composition controllable. Such composition was found to be able to affect the buffering ability of the materials, and the ratio of 1° : 2° : 3° amine = 1 : 4 : 1 is preferable for the pH buffering ability, also for the in vitro gene transfection. Up to 64 times higher TE than PEI was obtained in HeLa cells with the presence of 10% serum. Their excellent serum tolerance was also demonstrated by a bovine serum albumin (BSA) adsorption assay, in which much lower protein adsorption than 25 kDa PEI was observed. Structure-activity relationship studies also revealed that higher proportion of 2° amines may benefit the DNA binding ability, but the balance between the DNA condensation and release is more essential for non-viral vectors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...