Highly sensitive and stabilized sensing of 6-benzylaminopurine based on NiCo2O4 nanosuperstructures†
Abstract
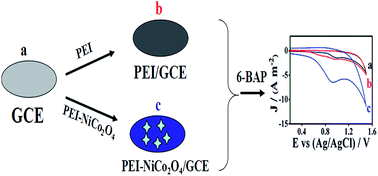
NiCo2O4 nanosuperstructures that were synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method were developed for the determination of 6-benzylaminopurine (6-BAP). As a novel electric material, NiCo2O4 can be utilized to structure an ultrasensitive and prominently stable electrochemical sensor. The electrochemical investigation confirmed that NiCo2O4 nanosuperstructures stabilized via polyethyleneimine (PEI) could remarkably boost the electrocatalytic activity for the oxidation response of 6-BAP owing to its unique properties of large pore volume, good electrical conductivity and metal catalysis. The detailed electrochemical behavior of 6-BAP at PEI-NiCo2O4/GCE exhibited a higher peak current and more negative oxidation potential than the bare glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Simultaneously, its kinetic and thermodynamic parameters were further calculated, indicating that this sensing platform accomplished excellent electrochemical catalysis towards 6-BAP. The fabricated sensor of PEI-NiCo2O4/GCE for 6-BAP presented a wide linear range from 10−10 to 10−5 M with a low detection limit of 0.1 nM. The modified electrode exhibited long-term stability and high sensitivity and showed good practicability for determining contamination in food and even broader applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...