Synthesis of SiO2 coated zero-valent iron/palladium bimetallic nanoparticles and their application in a nano-biological combined system for 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether degradation†
Abstract
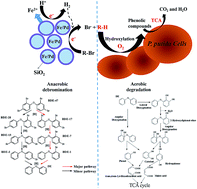
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are emerging persistent organic pollutants and the degradation of PBDEs is still a significant challenge owing to their extreme persistence and toxicity. In this study, the remediation of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE47) was investigated by employing a nano-biological combined system with SiO2-coated zero-valent iron/palladium bimetallic nanoparticles (SiO2-nZVI/Pd) as a reductant and Pseudomonas putida as a biocatalyst. The SiO2-nZVI/Pd exhibited much lower toxicity to the P. putida strain and higher reactivity in debromination than nZVI/Pd. The strain could grow well when the dosage was up to 1.0 g L−1. During the combined process, BDE47 (5 mg L−1) was completely debrominated to diphenyl ether (DE) within 2 h by SiO2-nZVI/Pd (1.0 g L−1) and then DE was completely degraded by P. putida after 4 days in sequential aerobic biodegradation. All the possible intermediates in the whole process were identified by ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS) analyses. The detection of BDE17, BDE7, BDE1 and DE indicated that rapidly stepwise debromination preferentially occurred at para positions in the anaerobic stage. Moreover, during aerobic biodegradation by P. putida, a number of phenolic compounds, such as phenol, catechol and hydroquinone were generated via ring opening by dioxygenation and further mineralized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA). Importantly, this combined process achieved rapid mineralization of PBDEs and avoided the generation of some highly toxic products like bromophenols and HO–PBDEs, which might have promising application prospects in the remediation of halogenated POPs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...