A new efficient technology for refractory phenol-formaldehyde resin wastewater treatment†
Abstract
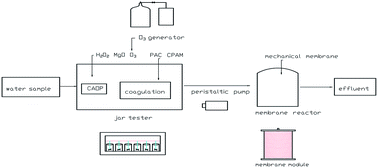
Phenol-formaldehyde resin wastewater contains high concentrations of phenol and formaldehyde, which have strong bio-resistance and toxicity to microbes, thus limiting the direct use of biological treatment methods. At present, studies on phenol-formaldehyde resin wastewater treatment are very few. The main objective of this study was to systematically evaluate the feasibility of O3/MgO/H2O2 – coagulation–mechanical membrane filtration process as a pretreatment method for such wastewater. The influence of several factors – including dosage of MgO powder as well as the concentrations of H2O2, O3, polyaluminum chloride (PAC) and cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) – was investigated. Experimental results indicated the optimal operational conditions were a 6 g L−1 dose of MgO powder, 5 g L−1 concentration of H2O2, 0.25 g L−1 min−1 dose of O3, 3 g L−1 of PAC, 30 mg L−1 of CPAM and use of a four-stage mechanical membrane. The concentrations of phenol and formaldehyde dropped to 28 mg L−1 and 43 mg L−1, respectively from the initial 4790 mg L−1 and 2660 mg L−1. The corresponding removal ratios were as high as 99.4% and 98.3%, respectively. Also, the residual turbidity was under 2.0 NTU and suspended solids (SS) could not be detected. The ratio of biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand (BOD/COD) increased from 0.165 to 0.364, indicating a good biodegradability. The effluent satisfied the requirements for direct access to the biochemical tank. Therefore, the combined process is a promising technology and may be used in the pretreatment of industrial phenol-formaldehyde resin wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...