Effects of C1–3-doping on electronic and structural properties of Stone–Wales defective boron nitride nanotubes as well as their NO gas sensitivity
Abstract
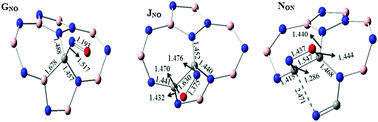
Doping nanotubes is a useful way to tune their electronic, optical and magnetic properties, and enhance their chemical reactivity for nanoelectronic device applications. In this work we investigate the electronic and structural properties of C-doped Stone–Wales (SW) defective (6,0) single-walled boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) at B3LYP/6-31+G(d) and M06-2X/6-31+G(d) levels of theory as well as their chemical sensitivity towards NO gas at ONIOM(M06-2X/6-31++G(d,p):M06-2X/STO-6G) levels. The different positions and concentrations of C dopant atoms are explored. Interaction energies and global reactivity descriptors are used to predict the overall reactivity of the studied C-doped SW-BNNTs. The results show that the doping of C at the neighboring B and N sites located in the 7-7 ring fusion (CNB and CNBB) leads to lower defect formation energies. In addition, we find that C impurities can substitute into the boron site due to the low formation energy. Owing to formation of the mid-gap states induced by substituting 3C atoms for three B atoms, a transformation from electrical insulator (band gap of 4.27 eV) to an electrical conductor (band gap of 1.65 eV) is predicted. Therefore, from these results it can be predicted that the 3CB-doped SW-BNNTs can be used to improve solar cell efficiency. The results obtained at M06-2X/6-31++G(d,p) level reveal that the NO adsorptions on the surface of C-doped SW-BNNTs are energetically favorable and are stronger than pristine and undoped SW-BNNTs. It is expected that the present results will provide a useful guide to develop novel C-doped BNNTs based sensors for the detection of toxic NO molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...