Ultrasonic-mediated synthesis and characterization of TiO2-loaded chitosan-grafted-polymethylaniline nanoparticles of potent efficiency in dye uptake and sunlight driven self-cleaning applications
Abstract
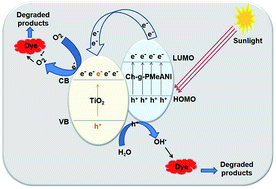
In the present study, a new sequential process for wastewater remediation in two steps with high durability was presented. Firstly, dye uptake on TiO2-loaded chitosan-graft-poly(2- and 3-methylaniline) nanocomposites was observed in the dark. Secondly, sunlight-assisted photocatalytic self-cleaning for regeneration of the used adsorbent was achieved. Thus a synergic effect of adsorption/photooxidation for successful removal of dye from aqueous solutions was manifested. The nanocomposites were characterized by FTIR, UV-Vis diffuse reflectance, XRD, and TEM. The data of dye adsorption were fitted to Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. The Langmuir model gave the best fit. The pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order were used to analyze the kinetic data. The data fit well with the second-order kinetic model. The adsorptive removal of the dye was highly efficient. Interestingly, the adsorbents were successfully regenerated by photomineralizing the adsorbed dye via solar-assisted self-cleaning. Efficient photocatalytic ability as reflected from the estimated photodegradation rate of the dye was observed. Furthermore, the prepared materials showed good photocatalytic stability after five runs under solar light. The ˙OH detected from the photoluminescence – terephthalic acid technique along with ˙O2− species seem to be the oxidizing species responsible for the sunlight-driven photodegradation reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...