Zirconium-promoted hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical porous carbons with ordered cubic mesostructures under acidic aqueous conditions†
Abstract
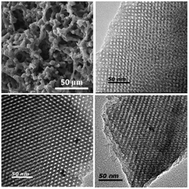
The zirconium-promoted hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical porous carbons with ordered cubic mesostructures (Im3m) under acidic aqueous conditions was first presented using F127 as a template, pre-synthesized resol as carbon precursor, hydrochloric acid as catalyst and zirconium oxychloride as an assistant agent. The effects of the zirconium oxychloride assistant, acid concentration, hydrothermal treatment time and treatment conditions on the structural properties of the hierarchical porous carbons were investigated. The results indicate that the zirconium polyoxo oligomers in the acid synthesis solution can suppress the condensation of the resols at a moderate rate around the micelles of F127 to form mesosporous carbon. Under hydrothermal conditions, zirconium polyoxo oligomers could interact with the polyethylene (PEO) chains of F127 through hydrogen bonding, increasing the hydrophilic/hydrophobic volume ratio and the interfacial curvature to promote the phase transformation of the mesostructure from 2-D hexagonal to 3-D body-centered cubic. With suitable acid concentration (1.0–3.0 M), hierarchical porous carbons with ordered cubic mesostructures can be synthesized in 8 h on a large scale. After activation with KOH, the equilibrium CO2 adsorption capacities of the resulting materials at 1 atm were in the range of 3.3–4.1 mmol g−1 at 25 °C and 4.8–6.6 mmol g−1 at 0 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...