Preparation of spherical agglomerates from potash alum
Abstract
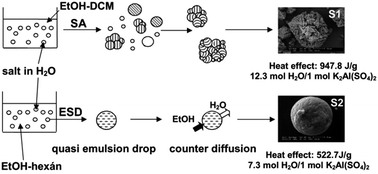
Salt hydrates are low-cost, readily available PCMs (phase change materials). As a core material for encapsulation the salt agglomerates can be prepared by spherical agglomeration, a well-known method to produce drug loaded microspheres in the pharmaceutical industry, but not used for PCM formulation. The two basic mechanisms in spherical crystallization are spherical agglomeration (SA) and the quasi emulsion solvent diffusion (QESD) processes. The spherical agglomerates of aluminium potassium sulfate dodecahydrate (potash alum dodecahydrate), a highly water soluble material, were produced by spherical crystallization technique in four different solvent systems. In water (good solvent)–ethanol–dichloromethane (poor solvent) ternary solvent system the agglomeration takes place by the SA mechanism. In water–ethanol–n-hexane, water–ethanol and water–isopropyl alcohol solvent systems spherical particles were produced by the QESD method. Both procedures were proved to be feasible for the preparation of spherical salt hydrate particles as core material for microencapsulation. This method gives important basis to produce phase change materials from suitable salt hydrates. The potash alum content in the spherical agglomerates was analysed by conductivity and thermogravimetric measurements and their composition by XRD. Volume weighted mean diameters (D(4,3)) of the microparticles were 66 μm, 79 μm, 89 μm, and 684 μm formed in water–ethanol–n-hexane, water–ethanol, water–isopropyl alcohol, and water–ethanol–dichloromethane solvent system, respectively. Potash alum dodecahydrate is a double salt. Due to its different solubility in the four different solvent systems it crystallized out not only as potash alum, but also in other salt forms. The enthalpy changes of spherical agglomerates produced from different solvent systems were increased proportionally with potash alum contents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...