A novel PEG–haloperidol conjugate with a non-degradable linker shows the feasibility of using polymer–drug conjugates in a non-prodrug fashion
Abstract
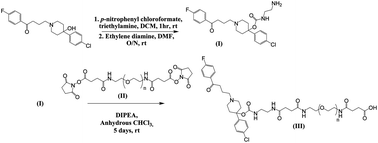
A PEG–haloperidol conjugate containing a non-biodegradable linker was synthesised. Incubation with rat plasma demonstrated excellent linker stability, and competition radioligand binding assays demonstrated retained binding to the D2-receptor. In silico studies predicted that the conjugate will not cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), thus potentially restricting haloperidol action to one side of the BBB.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...